The FireFly node
Table of contents
FireFly node runtimes
A FireFly node is a collection of multiple microservice runtimes with a single unified HTTPS/Websocket API (exposed by the Core).
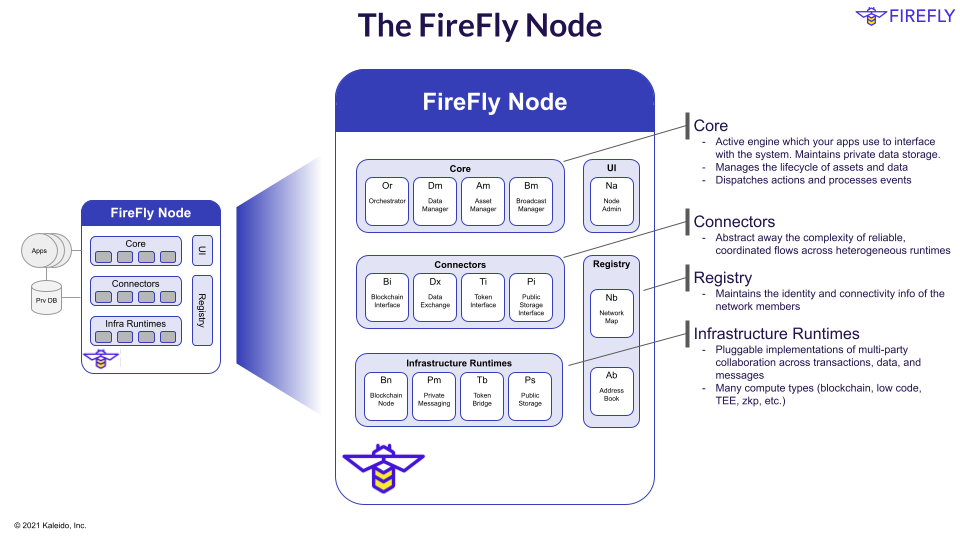
The minimum set of runtimes is as follows:
- FireFly Core - the API and event server for your multi-party applications
- Blockchain node - the decentralized ledger technology establishing a shared source of truth
- Blockchain interface - transaction submission and event streams for your chosen protocol
- Shared storage node - a network-wide peer-to-peer store of shared data
- Data exchange - for private member to member communications of messages and files
Check out the FireFly CLI to get a a multi-party system running on your laptop in minutes.
Pluggable microservices architecture
The runtimes are pluggable, allowing technology choice, and extensibility.
- FireFly Core
- Orchestration engine - manages lifecycle of assets and data
- Hosts the API and UI - applications connect here
- Maintains private storage
- Written in Go
- Connectors
- Runtimes that bridge the core to multi-party infrastructure
- Can be written in any language Go, Java, Node.js etc.
- Can be stateful or stateless, depending on requirements
- Can contain significant function, such as managed file transfer, or e2e encryption
- Infrastructure runtimes
- Can be local runtimes, or cloud services
- Blockchain nodes - Fabric, Ethereum, Corda etc.
- Database servers - PostreSQL, SQLite, CouchDB etc.
- Private messaging - Kafka, RabbitMQ, ActiveMQ, Mosquitto etc.
- Private blob storage - Kubernetes PVCs, AWS S3, Azure File etc.
- Public blob storage - IPFS, etc.
- … and more - token bridges, trusted compute engines, etc.